How is Cloud-based ERP different than Legacy Software?

ERP systems are a great resort to the traditional methods of manual resource planning and management. They substantially transform the work structure of an enterprise and instill a more standard and accurate management system.
Legacy and Cloud-based ERP are two variations of ERP that are often compared with each other. While Legacy ERP came first in the picture, Cloud-based ERP can be viewed as a technological upgrade to the same. However, each of them has its own distinct features.
In this blog, we will discuss how is cloud-based ERP better than legacy software?
The article will also walk you through the definitions of Legacy ERP, Cloud-based ERP and the differences between them.
What is an ERP?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a comprehensive software solution that organizations utilize to manage their daily operations, including procurement, accounting, human resources, manufacturing, and supply chain management. This suite of tools integrates, automates, and streamlines various organizational functions, leading to enhanced productivity and efficiency.
An ERP system offers a holistic view of the entire organization, enabling informed and strategic decision-making. By providing a centralized database, it allows businesses to access real-time information across all departments. This capability not only facilitates the generation of insightful reports but also enhances collaboration among teams by breaking down silos and ensuring that everyone is working with the same up-to-date data.
Core Functions of ERP
ERP systems are designed to streamline and automate various business processes, including:
- Finance and Accounting: Automates financial tasks, tracks accounts payable and receivable, and generates financial reports.
- Human Resources Management: Manages employee records, payroll, recruitment, and performance evaluations.
- Supply Chain Management: Oversees inventory management, procurement, and logistics to optimize product flow from suppliers to customers.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Enhances customer service through better management of customer interactions and data.
- Manufacturing: Coordinates production planning, scheduling, and quality control.
Current ERP Market Statistics 2024
The Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) market is experiencing significant growth, driven by the increasing demand for integrated business management solutions. Here are the key statistics and insights regarding the current state of the ERP market:
Market Size and Growth Projections
- 2024 Market Size Estimates:
Depending on the source, the ERP market is projected to reach between $65.25 billion and $183 billion in 2024. For instance, HG Insights estimates it at $183 billion, while Mordor Intelligence places it at $65.25 billion.
- Growth Rate:
The market is expected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of approximately 9.76% to 14.4% from 2024 to 2032, with varying estimates depending on the research firm.
- Long-Term Projections:
As businesses adopt advanced ERP solutions, the ERP market could reach between $238.79 billion (Fortune Business Insights) and $311.4 billion (The Business Research Company) by 2028.
Regional Insights
- North America:
This region leads in ERP spending, with a projected worth of over $78.7 billion in 2024. Major players like Microsoft, Oracle, and SAP dominate this market.
- Asia-Pacific:
Expected to be the fastest-growing region for ERP systems, driven by a burgeoning startup ecosystem and manufacturing sector.
Market Segmentation
- Key Segments:
The financial applications segment commands a significant share, estimated at around $38.5 billion, while customer relationship management (CRM) systems account for approximately $40.5 billion.
- Adoption Trends:
There is a noticeable shift towards cloud-based ERP solutions, which facilitate real-time data access and improved operational efficiency. This trend is particularly pronounced post-COVID-19 as businesses adapt to digital transformation needs.
Types of ERP Systems
| Type of ERP System | Description |
| On-Premise ERP | Software installed on company servers, providing full control over the system and data management. |
| Cloud ERP | Hosted on remote servers, accessed via the internet, offering scalability and lower upfront costs. |
| Hybrid ERP | Combines elements of both on-premise and cloud systems, allowing for flexibility in data management. |
| Industry-Specific ERP | Tailored for specific industries (e.g., manufacturing, retail) with specialized features and terminology. |
| Open Source ERP | Source code is available for customization; typically requires more technical expertise to maintain. |
| Small Business ERP | Designed specifically for small to medium-sized businesses, balancing essential functionalities with cost. |
| Multi-Cloud ERP | Utilizes multiple cloud services for enhanced flexibility and integration across various platforms. |
| ERP in a Box | Pre-packaged solutions that are easy to implement but offer limited customization options. |
| Tiered ERP | Offers varying levels of functionality based on business size and needs, allowing for scalable solutions. |
What is Legacy ERP?
Legacy ERP or Legacy Enterprise Resource Planning System consists of robust specifications for business management. However, it needed constant upgrades to meet the evolving industry standards.
As a result, the creators of the product needed to continually come up with codes to meet the requirements of their existing customers.
This process became tedious for both the creators and the consumers, and Legacy ERP was eventually declared to be outdated.
You may also like to read : What is ERP and Why is it Used in a Company?
What is Cloud-based ERP?
Cloud ERP is an upgrade to the traditional Legacy ERP system. Unlike an on-premise system, it is not limited to a network or location. It is linked to a cloud platform that allows the user to access the portal in a remote and flexible manner.
A cloud-based ERP system automates different office processes and integrates them into a common platform. This inculcates convenience and efficiency in the workspace.
Legacy Versus Cloud ERP
The major differences between Legacy ERP and Cloud-based ERP are highlighted through the methods of installing and assessing the software. Cloud ERP presents a more convenient interface in terms of access and flexibility as compared to Legacy ERP.
Legacy ERP works with network servers and system restrictions. These are the fundamental distinctions between the two kinds.
Let’s have a look at some more differences stated below-
Cost, Time & Effort
Cloud ERP is available as SaaS, i.e., Software as a service. It allows the user to enjoy an integrated work platform by paying a subscription fee. The user gets access to the software portals and tools and the freedom to use the application on any hardware device or network server. It also gives the user the liberty to select from different plans and purchase the package that suits the buyer’s requirements and budget.
Software like Juntrax is a prime example of comprehensive and user-friendly software that does not require any expertise and can easily be operated by anyone having a basic understanding of IT and technology.
You may also like to read : Affordable and Complete ERP Solution for SMEs
In contrast to cloud-based ERP systems, Legacy ERP requires the user to purchase the software along with the hardware. In case if the office does not have a well-maintained hardware system, they will have to invest in building one, if they wish to install the software. They can not be operated with basic knowledge and therefore require a dedicated team of professionals.
Upgrades and Customizations
Most of the companies offering legacy and cloud ERP systems, provide an option to upgrade and customize the software as per the requirements of the company.
In the case of a cloud-based ERP system, updates can be handled easily as the process is automated and directly handled by the vendor via the cloud.
However, in the case of Legacy ERP, the user or the manager is required to look after the updates and manage them. The updates need a well-versed IT team in order to get installed and implemented. Therefore, it becomes complicated to get a Legacy ERP updated in comparison to a cloud-based ERP.
Mobile Access
Cloud-based ERPs can be accessed through Internet browsers and are therefore advantageous in terms of remote access. They are not restricted to a server and can be used anywhere at any time. They are also flexible and can be used on interfaces like Windows, Android, iOs, and Apple. Many Cloud-based ERPs come with mobile applications to further simplify the user experience.
You may also like to read : Reasons why your organization must have a Mobile ERP
In the case of a Legacy ERP also known as On-premise ERP, the user can only access it on the device on which it has been installed. It also has network restrictions and only functions on authorized servers.
ERP Implementation Statistics 2024
- Consultant Engagement: Companies that hired software consultants for their ERP implementation achieved an 85% success rate. This underscores the importance of expert guidance in navigating complex ERP projects.
- Leadership Support: Among organizations that completed an ERP implementation, 77% identified institutional leadership support as the most critical success factor. 60% of respondents also highlighted effective communication with stakeholders as essential for success.
- Implementation Approaches: Only 21% of organizations utilized a “big bang” approach, where all system components go live simultaneously. In contrast, over 50% opted for a phased approach, which is generally seen as less risky and more manageable.
How is Cloud-based ERP better than legacy software? – Difference
|
Legacy ERP |
Cloud-based ERP |
|
| 1 | They function on hardware infrastructure and require system installations. | They do not need on-premise installation and function on a cloud interface on any Internet server |
| 2 | They are created with the help of a proprietary or legacy programming language. These languages tend to get outdated and discontinued in the future. | They are developed using prominent web-based tools like java and HTML. These languages will never get outdated and therefore present a long-term advantage. |
| 3 | Legacy ERP software can only be installed manually with the help of CDs. | Most of the cloud-based ERP software are installed with the help of a cloud without any manual struggle. |
| 4 | Implementing a Legacy ERP requires a considerable amount of time as every process is performed and managed manually. | Cloud-based ERP software have a pre-built design and perform in an automated manner. They also offer an integrated interface and therefore save a considerable amount of time and effort. |
| 5 | Applications of a Legacy ERP require periodic updates and therefore incur extra cost, time, and effort. | Applications of a cloud-based ERP get updated, administered, and maintained in an automated discourse on a periodic basis. |
| 6 | It is not very cost-effective | It is very Cost-Effective |
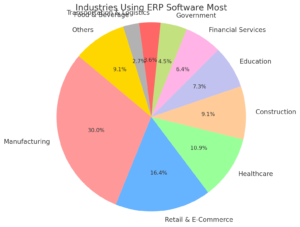
Which Industries use ERP Software most?
- Manufacturing: ERP used for production, supply chain, inventory, procurement, distribution (33% of users).
- Retail & E-Commerce: ERP used for inventory management, CRM, sales tracking, supply chain (18% of users).
- Healthcare: ERP used for patient records, financials, HR, supply chain logistics (12% of users).
- Construction: ERP used for project management, procurement, accounting, HR, contracts (10% of users).
- Education: ERP used for student records, financial aid, payroll, HR, asset management (8% of users).
- Financial Services: ERP used for accounting, investments, payroll, compliance (7% of users).
- Government: ERP used for financials, HR, procurement, public works (5% of users).
- Transportation & Logistics: ERP used for fleet, logistics, warehouse management, financial tracking (4% of users).
- Food & Beverage: ERP used for inventory, supply chain, food safety compliance (3% of users).
- Others: ERP used in energy, telecom, professional services (10% of users).
Conclusion
The market is filled with rigorous competition and to stay ahead of all your competitors it is important to know your needs, enhance your workspace and adopt technology that will boost the potential of your enterprise.
An ERP system fulfills those requirements. The decision to select between a cloud-based ERP and a Legacy ERP must be made after carefully assessing your needs, your budget, the workspace, and the future prospects of your enterprise. A Cloud-based ERP can be your shield on the battlefield while a Legacy ERP might slow down your pace.
FAQs
How is Cloud-based ERP more cost-effective than Legacy ERP?
Answer:
Cloud-based ERP typically follows a subscription-based pricing model, eliminating the need for large upfront investments in hardware and software. On the other hand, legacy ERP systems require significant capital expenditure for purchasing and maintaining servers, along with ongoing IT support costs. Cloud-based ERP also reduces costs related to updates, as the provider manages them.
How does scalability differ between Cloud-based ERP and Legacy ERP?
Answer:
Cloud-based ERP is highly scalable, allowing businesses to add new users, modules, or features as needed, often with just a few clicks. Legacy ERP systems are less flexible, requiring physical upgrades to hardware or significant customizations to the software to accommodate growth or changing business needs.
Which ERP system offers better data accessibility, Cloud-based ERP or Legacy ERP?
Answer:
Cloud-based ERP allows users to access the system from anywhere, as long as they have an internet connection. This makes it ideal for remote work and real-time data access. Legacy ERP systems are typically limited to on-premises access, which can be restrictive for businesses with multiple locations or employees who need remote access.
Is Cloud-based ERP more secure than Legacy ERP?
Answer:
Cloud-based ERP providers often have high levels of security measures in place, such as data encryption, regular backups, and security updates, ensuring data protection. In contrast, Legacy ERP systems place the responsibility of security entirely on the business, which might not have the same level of resources for comprehensive protection against modern cybersecurity threats.
Which system has easier maintenance and updates: Cloud-based ERP or Legacy ERP?
Answer:
Cloud-based ERP requires minimal maintenance on the user’s end, as the provider manages updates, security patches, and system upgrades automatically. Legacy ERP systems often require manual updates, which can be time-consuming and costly, often leading to downtime or compatibility issues if not handled properly.
Can Cloud-based ERP integrate with other modern software tools better than Legacy ERP?
Answer:
Yes, cloud-based ERP is typically built with modern APIs allowing easier integration with cloud-based tools like CRM, e-commerce platforms, and payroll systems. Legacy ERP systems may require custom-built integrations, which can be more difficult and expensive to implement.
Which is more suitable for smaller businesses: Cloud-based ERP or Legacy ERP?
Answer:
Cloud-based ERP is generally more suitable for smaller businesses due to its lower upfront costs, scalability, and ease of use. Legacy ERP systems are better suited for larger companies that may have the infrastructure and resources to maintain and customize their systems extensively.
What are the deployment time differences between Cloud-based ERP and Legacy ERP?
Answer:
Cloud-based ERP can be deployed much faster, sometimes within weeks, because there is no need for complex hardware installation or lengthy software customizations. Legacy ERP, on the other hand, can take months or even years to fully implement due to hardware requirements, customizations, and configurations.