What is Compensation Management and Why is it Important?

In any workplace, compensation isn’t just about paychecks—it’s a fundamental aspect of an organization’s strategy. Compensation management is the systematic approach to planning, distributing, and overseeing employees’ rewards, including salary, benefits, bonuses, and other incentives.
This function has become increasingly essential as organizations recognize that employee compensation significantly influences attraction, retention, and motivation.
Effective compensation management is crucial in today’s evolving job market, where transparency, equity, and flexibility are highly valued. It enables organizations to remain competitive, build a motivated workforce, and align compensation structures with organizational goals and values.
What is Compensation Management?
Compensation management refers to the organization’s process of designing and managing the monetary and non-monetary benefits employees receive for their work. It involves developing structured pay practices, implementing reward systems, and periodically adjusting compensation levels to meet both employee expectations and business goals.
Moreover, it guarantees that each employee receives a fair wage reflecting industry standards, work experience, the company’s budget, and other relevant factors.
As of September 2024, compensation costs for civilian workers increased by 3.9% over the past year, with wages and salaries also rising by 3.9%. This reflects a slowdown compared to a 4.3% increase in 2023.
Components of Compensation
- Direct Compensation: This includes all direct forms of payment employees receive. Examples are:
- Salaries: Fixed payments made regularly, like monthly or biweekly.
- Bonuses and Incentives: Additional payments are given for meeting certain performance metrics or achieving specific targets.
- Stock Options and Profit-Sharing: Equity-based rewards that allow employees to participate in the company’s financial success.
- Indirect Compensation: These are non-monetary benefits that still hold significant value. Examples are:
- Health Insurance: Medical, dental, and vision coverage, which are essential for employee health and satisfaction.
- Retirement Plans: Contributions to a retirement fund, such as 401(k) plans, which offer long-term financial security.
- Paid Leave: Time off such as vacation days, sick leave, and parental leave. Providing generous paid leave enhances work-life balance, which is a key factor in job satisfaction.
- Total Compensation: This concept integrates both direct and indirect compensation to provide a comprehensive view of what employees receive. It is essential for attracting and retaining talent, as it reflects the full value of employment beyond just salary.
Types of Compensation Plans

- Fixed Pay: A predetermined, stable amount paid to employees regardless of performance. Examples are salaries and hourly wages.
- Variable Pay: Compensation that varies based on employee or company performance, often tied to metrics or sales targets.
- Skill-Based Pay: Compensates employees based on specific skills or certifications that add unique value to the company.
- Performance-Based Pay: Tied directly to performance results, incentivizing employees to exceed goals and meet higher standards.
Key Factors Affecting Compensation Management
Compensation management is influenced by many factors that organizations must consider to establish fair, competitive, and effective remuneration strategies.
Understanding these factors is crucial for HR professionals and business leaders alike, as they directly impact employee satisfaction, retention, and overall organizational performance.
1. Industry Standards
The industry in which a company operates significantly affects compensation levels. Different sectors have varying pay scales based on the nature of the work, required skill sets, and market demand for talent.
For instance, technology and finance sectors often offer higher salaries compared to retail or hospitality industries due to their specialized nature and the competitive landscape for skilled workers.
2. Education and Experience
An employee’s educational background and professional experience are critical determinants of their compensation. Generally, higher education levels and extensive experience correlate with increased pay.
For example, individuals with advanced degrees or significant industry experience typically command higher salaries than entry-level employees.
3. Job Title and Responsibilities
The specific job title and associated responsibilities are vital in determining compensation. Senior positions with greater responsibilities, such as executives or managers, are compensated more than entry-level roles.
Job evaluations help assess the relative worth of different positions within an organization, ensuring that compensation aligns with the level of responsibility.
4. Performance Metrics
Employee performance is a key factor in compensation management. Organizations often link compensation to performance metrics, rewarding high-performing employees with bonuses, raises, or promotions.
This performance-based approach incentivizes productivity and aligns employee goals with organizational objectives.
5. Market Trends
Staying informed about market trends is essential for competitive compensation management. Companies must regularly benchmark their pay structures against industry standards to ensure they attract and retain top talent.
Organizations may struggle to fill critical roles if competitors offer better compensation packages.
6. Geographical Location
The geographical location of a job significantly influences compensation due to variations in the cost of living. Employees in high-cost areas typically receive higher salaries to offset living expenses than those in regions with lower living costs.
This geographic pay adjustment helps maintain employee satisfaction and retention.
7. Labor Market Dynamics
The labor market’s supply and demand dynamics also affect compensation levels. In industries where there is a shortage of skilled labor, employers may need to offer higher wages to attract qualified candidates.
Conversely, an oversupply of labor can lead to lower wages as competition for jobs increases.
8. Company Financial Health
An organization’s ability to pay is influenced by its financial health and profitability. Financially stable companies can afford to offer more competitive salaries and benefits packages compared to those facing economic challenges or operating at a loss.
9. Government Regulations
Government policies and regulations regarding minimum wage laws, overtime pay, and employee benefits also significantly shape compensation management strategies. Organizations must comply with these regulations while designing their compensation packages to avoid legal repercussions.
10. Company Culture and Values
The internal culture of an organization influences its approach to compensation management. Companies that prioritize employee well-being may offer comprehensive benefits packages that include health insurance, retirement plans, and work-life balance initiatives over higher salaries alone.
This holistic approach can enhance employee loyalty and satisfaction.
Why is Compensation Management Important?
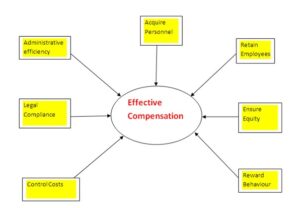
Effective compensation management plays a central role in shaping a productive, motivated, and loyal workforce. It goes beyond simply paying employees; compensation management creates a strategic system that aligns employee motivation with organizational goals, attracts top talent, and reinforces a culture of fairness and transparency.
1. Retaining Top Talent and Building Loyalty
Compensation management directly impacts employee retention. Employees who feel fairly compensated tend to stay with the organization longer, which reduces turnover and the high costs of rehiring and training new staff. Compensation remains one of the strongest drivers of employee satisfaction and loyalty.
When companies offer competitive pay and benefits packages, they build trust and goodwill, encouraging employees to commit long-term to the organization.
A strong retention strategy reduces disruptions and maintains high organizational knowledge and stability. Through effective compensation management, companies create a loyal workforce that contributes to long-term success.
2. Driving Employee Productivity and Performance
Well-structured compensation management motivates employees to perform at their best. When employees understand that their efforts and achievements directly affect their compensation, they feel incentivized to contribute more effectively.
Companies that link compensation to specific performance metrics foster a results-driven culture.
For instance, performance-based bonuses, commission structures, or milestone rewards encourage employees to exceed their goals. By connecting pay to performance, companies channel employees’ efforts toward activities that drive organizational success.
Employees who reach higher standards improve productivity, efficiency, and the overall bottom line.
3. Enhancing Job Satisfaction and Morale
Compensation management plays a vital role in building employee morale and job satisfaction. Employees who receive fair pay feel valued and appreciated for their contributions, which boosts workplace morale.
Fair and transparent compensation practices also create a positive work culture where employees feel secure and respected.
Satisfied employees tend to engage more actively in their roles, approach tasks enthusiastically, and show greater commitment to their work.
By addressing employees’ financial and personal needs, effective compensation management helps companies foster a motivated and energized workforce, which improves the overall workplace atmosphere.
4. Attracting Quality Talent
A strong compensation management strategy helps companies attract the best talent in their industry. Today’s job market is highly competitive, and skilled candidates often compare compensation packages before choosing an employer.
Companies that offer attractive compensation packages stand out to top candidates and gain a significant advantage in hiring highly skilled individuals. Competitive compensation signals that the company values its workforce, making it an appealing choice for job seekers.
Through effective compensation management, companies build their reputation as desirable employers, increasing their ability to attract high-quality, skilled, and motivated employees.
5. Ensuring Fairness and Transparency
Compensation management creates a framework for fairness and transparency in how the organization rewards its employees. When companies establish clear, structured pay policies, they build trust with their employees and create an environment of fairness.
Transparent pay practices reduce resentment and tension, especially when employees understand how the company determines pay levels and rewards. Fairness and transparency in compensation management also support equity initiatives, ensuring that employees receive equal pay for equal work regardless of gender, race, or other characteristics.
This focus on fairness promotes an inclusive culture and strengthens trust within the workforce.
6. Supporting Legal Compliance and Reducing Risk
Compensation management protects the organization from legal risks by ensuring compliance with labor laws and wage regulations. Laws around minimum wage, overtime, equal pay, and other compensation practices require companies to adhere to specific standards.
Compensation management allows HR teams to monitor and adjust pay practices regularly, ensuring that the organization complies with all legal requirements. By following fair pay practices and staying up-to-date with changes in labor laws, companies avoid fines, lawsuits, and reputational damage.
A compliance-focused approach to compensation management builds a foundation of trust and credibility, which benefits both employees and the organization.
7. Aligning Employee Efforts with Organizational Goals
Compensation management aligns employee efforts with the company’s strategic goals, ensuring that everyone works toward the same objectives. When compensation ties directly to performance and key business outcomes, employees focus their efforts on the company’s priorities.
For example, a company aiming to increase customer satisfaction may offer incentives for customer service teams to achieve high satisfaction ratings. By designing compensation strategies that reflect business goals, organizations create a clear connection between individual contributions and overall success.
This alignment fosters a unified direction, increases employee engagement, and strengthens the company’s competitive position in the market.
8. Controlling Costs and Maximizing Financial Efficiency
Effective compensation management helps companies control costs while maximizing their return on investment (ROI) in human capital. Compensation accounts for a significant portion of an organization’s budget, and efficient management ensures that these funds support both employee satisfaction and business priorities.
By analyzing pay structures and benchmarking against market standards, companies identify opportunities to optimize compensation without overspending.
This approach allows organizations to offer competitive pay for high-impact roles while managing overall compensation costs.
Key Components of a Successful Compensation Management Strategy
- Benchmarking and Market Research: This involves understanding industry standards, analyzing competitor pay scales, and using this data to make informed decisions. Benchmarking helps the company remain competitive and attracts the right talent by offering pay consistent with market rates.
- Job Analysis and Evaluation: Thorough job analyses help establish fair pay based on the value and requirements of each role. This ensures that each job is compensated appropriately for its responsibilities, qualifications, and contributions.
- Performance Management Alignment: Linking compensation to performance metrics, such as achieving sales targets or completing projects on time, ensures that compensation rewards measurable achievements. This fosters a results-oriented work culture.
- Internal Equity vs. External Competitiveness: Balancing internal equity (ensuring fair pay within the organization) with external competitiveness (offering market-aligned pay) is key. Internal equity supports employee fairness, while external competitiveness helps attract new talent.
- Transparent Communication and Feedback: Open communication regarding compensation policies builds trust, ensuring employees understand and accept how their compensation is determined. Transparency helps prevent misunderstandings and promotes a positive organizational culture.
Role of Technology in Compensation Management
- Compensation Management Software: Software platforms like Juntrax simplify compensation management by centralizing data and automating tasks like payroll, performance reviews, and compliance checks. These tools help HR teams efficiently manage complex pay structures and employee benefits.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Advanced software solutions offer analytics, helping HR teams make evidence-based decisions on salaries, pay adjustments, and budgets, ensuring a fair and transparent system.
- Streamlined Processes: Automation speeds up time-consuming processes like compensation reviews, approvals, and compliance checks, minimizing human error and reducing administrative burden.
- Real-Time Market Analysis: Many compensation software solutions provide access to real-time market data, helping HR adjust compensation based on the latest industry benchmarks. This ensures that organizations remain competitive in a fast-changing market.
Challenges in Compensation Management
- Budget Constraints vs. Competitive Pay: Striking a balance between budget limitations and the need for competitive compensation is challenging. Organizations must strategically allocate funds to ensure fair compensation without overspending.
- Pay Equity and Closing the Gender Pay Gap: Addressing pay disparities is essential for promoting equality and retaining diverse talent. Achieving pay equity requires ongoing analysis and adjustments, often involving significant changes to existing pay structures.
- Adapting to Remote and Hybrid Work Models: With remote work becoming more common, compensation management must address challenges like location-based pay adjustments and differentiating pay for remote versus in-office roles.
- Transparency and Data Security: Ensuring transparency while safeguarding compensation data from breaches is crucial. Organizations must balance openness about pay policies with strict data protection to maintain employee trust and regulatory compliance.
Best Practices for Effective Compensation Management
- Regular Review and Adjustment: Organizations should routinely assess and adjust pay structures based on market changes, organizational growth, and employee feedback to ensure ongoing competitiveness.
- Employee Feedback and Engagement: Engaging employees through surveys or feedback sessions helps HR teams understand employee perspectives, fostering greater acceptance and satisfaction with compensation decisions.
- Compliance Audits: Regular audits help identify potential compliance issues with labor laws and wage regulations, reducing the risk of legal repercussions and ensuring fair treatment.
- Professional Development and Reward Systems: Aligning compensation with opportunities for career growth and skill development encourages long-term retention and helps employees see value beyond monetary rewards.
Bottom Line
A well-managed compensation strategy is essential for creating a motivated, loyal, and productive workforce. When organizations invest in fair and competitive compensation systems, they create a workplace where employees feel valued and aligned with the organization’s goals.
Regularly assessing and refining compensation strategies also enables companies to keep up with market trends, ensuring that they remain attractive to both current and prospective employees.
As companies grow and evolve, revisiting compensation practices and ensuring alignment with organizational goals and employee expectations remains vital.
One thought on “What is Compensation Management and Why is it Important?”
Comments are closed.