What is Management by Objectives (MBO)
The concept of “Management by Objectives” (MBO) is rooted in a simple yet powerful idea: aligning individual goals with organizational objectives leads to success.
Picture this—everyone, from entry-level employees to top management, working toward shared goals that drive the company forward. It sounds seamless, but achieving this alignment takes strategy and commitment.
Management by Objectives, often referred to as MBO, is a structured approach that helps companies connect the dots between personal performance and overall business success. In this article, we’ll break down how MBO works, from setting clear, measurable objectives to tracking progress and celebrating achievements.
We’ll also cover the benefits and potential challenges of implementing MBO, giving you a full picture of its impact on the modern workplace.
What is Management by Objectives (MBO)?
Management by Objectives (MBO) is a strategic management framework that focuses on the collaborative establishment of goals between management and employees.
This approach aims to align individual performance with the organisation’s broader objectives, enhancing productivity, accountability, and overall operational effectiveness.
You may also like to read : What is Performance Management System ?
Types of Objectives in MBO
In the MBO framework, objectives can be categorized into three main types:
- Strategic Objectives: Long-term goals aligned with the organization’s vision, typically spanning three to five years. These high-level objectives guide overall direction.
- Tactical Objectives: Shorter-term goals that support strategic objectives, often focused on specific departments or teams.
- Operational Objectives: Day-to-day goals that ensure tactical plans are executed effectively, contributing to achieving broader organizational aims.
Background on MBO
Management by Objectives (MBO) was developed in the 1950s by management consultant and author Peter Drucker. Recognizing a need for companies to work toward clear and collective goals, Drucker introduced MBO as a way to unify teams around measurable objectives.
His idea represented a shift from traditional top-down management styles, emphasizing goal-setting as a collaborative process that engages employees at all levels. This strategic alignment aimed to ensure that every action taken within an organization contributes meaningfully to its overall mission.
Drucker’s concept of MBO quickly gained traction as an effective management model, leading many companies to adopt it to improve focus, productivity, and accountability.
Core Concept of Management by Objectives (MBO)
At its core, Management by Objectives is a strategic management model that prioritizes setting, tracking, and achieving specific, measurable goals. In MBO, leaders and employees work together to define objectives that are both ambitious and attainable, ensuring that each goal directly supports the company’s larger objectives.
This model empowers employees to take ownership of their targets, promoting an environment of commitment and shared purpose.
MBO relies on transparency, where every team member knows their objectives and the metrics used to measure success. By defining goals collaboratively, MBO transforms the planning process into an inclusive one, enabling everyone to understand their role in the company’s success.
The Core Principles of Management by Objectives (MBO)
SMART Goals
Setting SMART goals is fundamental to the MBO framework. The SMART acronym stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-Bound. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring that objectives are clear and attainable:
- Specific: Goals must be well-defined and unambiguous. A specific goal answers the questions of who, what, where, when, and why. For instance, instead of stating “increase sales,” a specific goal would be “increase sales by 15% in the Northeast region by Q3.”
- Measurable: Criteria should be established for measuring progress toward the goal. This allows managers and employees to track advancements and make necessary adjustments. For example, a measurable goal might state, “achieve a customer satisfaction score of 90% in quarterly surveys.”
- Achievable: Given the available resources and constraints, goals should be realistic and attainable. While they should challenge employees, they must also be within reach to maintain motivation.
- Relevant: Each goal should align with broader organizational objectives. This ensures that individual efforts contribute meaningfully to the company’s mission.
- Time-Bound: Goals need a clear timeframe for completion. This creates urgency and helps prioritize tasks effectively. For example, stating “complete the project by December 31” provides a specific deadline.
Adhering to these criteria can help organizations enhance clarity and focus in their goal-setting processes, leading to improved performance outcomes.
Top-Down and Bottom-Up Approach
MBO fosters collaboration through a combination of top-down and bottom-up approaches in setting objectives:
- Top-Down Approach: Senior management establishes broad organizational goals that cascade down through various organizational levels. This ensures that everyone understands the overarching objectives and how their roles contribute to achieving them.
- Bottom-Up Approach: Employees at all levels are encouraged to participate in the goal-setting process. Their insights into operational realities help create realistic objectives that consider on-the-ground challenges. This mutual agreement between managers and employees fosters ownership and accountability.
The synergy of these approaches results in well-rounded objectives that reflect both strategic priorities and practical considerations. Engaging employees in this process enhances commitment and improves morale as they feel valued and contribute to the organization’s success.
Continuous Monitoring and Feedback
An essential aspect of MBO is the iterative feedback loop that supports continuous improvement:
- Regular Check-Ins: Scheduled meetings between managers and employees provide opportunities to discuss progress toward goals. These check-ins allow for adjustments based on changing circumstances or challenges encountered.
- Real-Time Feedback: Continuous feedback helps identify areas for improvement early on, enabling timely interventions that can steer efforts back on track.
This ongoing dialogue ensures that goals remain relevant and achievable while fostering an environment of open communication. It also empowers employees to take ownership of their development by actively discussing their performance.
Evaluation and Rewards
MBO places significant emphasis on performance evaluation linked to rewards:
- Performance Assessments: Evaluations are conducted based on achieving pre-defined objectives rather than subjective measures. This objectivity promotes fairness in assessing employee contributions.
- Tying Success to Rewards: Successful attainment of goals often leads to tangible rewards such as bonuses, promotions, or recognition programs. This alignment between performance outcomes and rewards motivates employees to strive for excellence.
By clearly linking evaluations with rewards, organizations can cultivate a high-performance culture where employees are incentivized to meet or exceed their objectives. This not only drives individual performance but also contributes to overall organizational success.
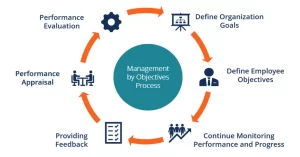
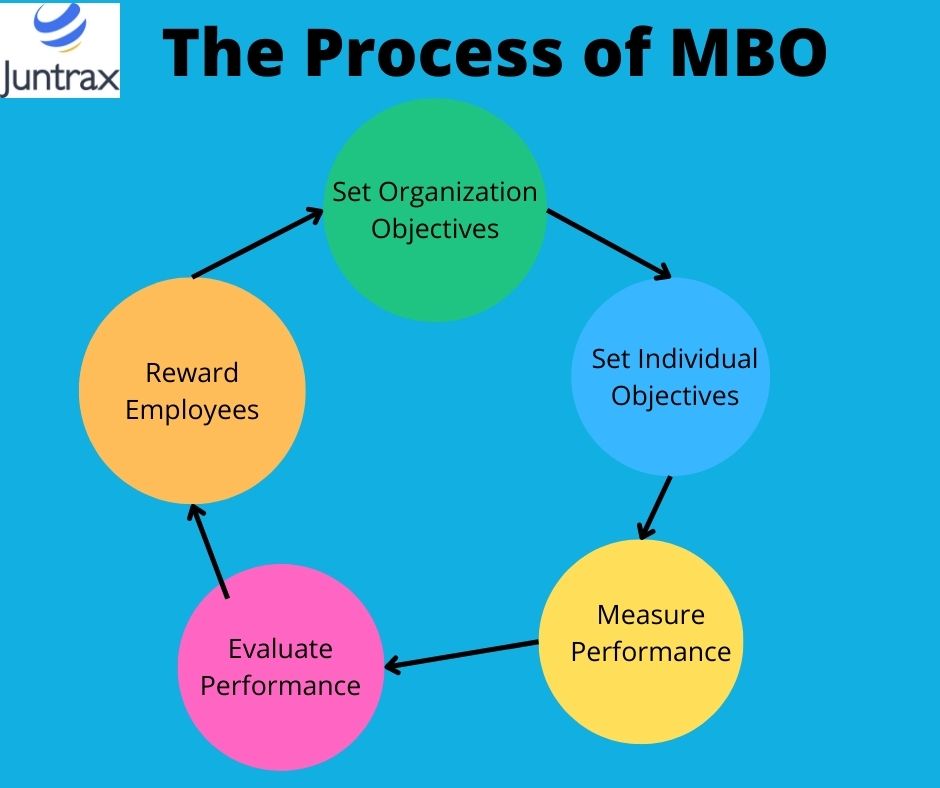
The MBO Process – How It Works
Setting Organizational Objectives
The MBO process begins with defining clear and strategic objectives at the organizational level, setting the foundation for everything that follows. These high-level goals represent the company’s mission, vision, and priorities, providing a roadmap for teams and individuals to follow.
Leadership identifies key objectives that align with the organization’s long-term strategy and values, whether focused on growth, innovation, customer satisfaction, or operational excellence.
By establishing these broad, overarching goals, MBO ensures that every objective set within the company supports a cohesive direction.
These organizational objectives act as the guiding principles for the entire workforce, ensuring that all subsequent goals reinforce the company’s purpose and ambitions.
Defining Individual Goals
Once the company’s overall objectives are in place, managers and employees collaborate to define individual goals that align with these larger aims. In MBO, this process is crucial because it directly links personal performance and organizational success.
Managers work closely with each employee to set specific, measurable goals tailored to their role, skills, and responsibilities. This approach personalises the objectives and empowers employees by involving them in the goal-setting process.
Employees gain clarity on their tasks and understand how their efforts contribute to the company’s vision, creating a sense of purpose and ownership.
Through these personalized objectives, MBO fosters alignment across all levels of the organization, turning the broader company goals into actionable steps for every individual.
Regular Monitoring
Ongoing monitoring is pivotal in the MBO process, allowing managers and employees to track progress and stay aligned with their targets. Regular progress reviews, typically conducted monthly or quarterly, provide an opportunity to evaluate achievements, identify challenges, and make necessary adjustments.
These check-ins ensure that employees remain focused and motivated, while managers gain insights into the team’s performance and any support they may need to stay on track.
This continuous feedback loop prevents goals from becoming stagnant or misaligned, as adjustments can be made in real-time to reflect changing circumstances or priorities.
By keeping the lines of communication open, MBO transforms monitoring into a proactive process that drives improvement and resilience.
Evaluating Performance
Performance evaluation in MBO is a structured and objective-driven process that assesses individual and team success based on achieving established goals. At the end of each cycle, managers and employees come together to review the objectives set at the beginning, examining the results, accomplishments, and areas for growth.
Managers use objective criteria to evaluate performance, focusing on measurable outcomes rather than subjective assessments. This approach creates transparency and fairness, allowing employees to see how their efforts translated into results.
Performance evaluations in MBO are not just a formality but a developmental tool; they provide employees with valuable insights into their strengths and opportunities for improvement.
By grounding evaluations in clearly defined metrics, MBO fosters a culture of accountability and growth, encouraging everyone to strive for continuous improvement.
Rewarding Success
Rewarding achievement forms a vital part of the MBO process, reinforcing the value of hard work and motivating employees to achieve their objectives. When employees meet or exceed their goals, organizations often tie these accomplishments to tangible rewards, such as bonuses, promotions, or other incentives.
These rewards acknowledge individual success and emphasize the company’s commitment to recognizing contributions that drive organizational progress.
Through rewards, MBO creates a direct link between performance and recognition, boosting morale and encouraging employees to remain committed to their goals.
This emphasis on rewarding success contributes to a positive, results-oriented culture where employees feel valued for their achievements, driving a sustained commitment to excellence and goal attainment.
Management by Objectives Examples
Management by Objectives (MBO) is a powerful framework that organizations can use to enhance performance through clear goal-setting and collaboration between management and employees.
Below are several practical examples of how MBO can be effectively implemented across different departments and industries.
Sales Department Examples
- Decrease Sales Cycle: A sales team might set an objective to reduce the sales cycle from four months to two months. This goal can be broken down into actionable steps, such as improving lead qualification processes and enhancing follow-up strategies.
- Increase Average Sales Value: The team could aim to raise the average sale value to $10,000 by implementing upselling techniques and focusing on high-value clients. Specific training sessions could be scheduled to equip the team with the necessary skills.
- Customer Acquisition Goals: Setting a target to bring in 15 new customers within a quarter can help focus efforts on lead generation and conversion strategies. Each sales representative might have individual targets aligned with this overall goal.
Marketing Department Examples
- Social Media Engagement: A marketing team may set an objective to increase social media likes by 40% over six months. This could involve creating engaging content, running targeted ad campaigns, and analyzing engagement metrics regularly.
- Website Metrics Improvement: The goal could be to increase the average time spent on the website by five minutes. Strategies might include enhancing content quality, improving site navigation, and adding interactive elements.
- Lead Generation: A marketing department might aim to generate 500 new monthly leads through various campaigns. This objective would require collaboration with sales to ensure that leads are effectively nurtured and converted.
- Media Placements: Another objective could be to secure five media placements in reputable publications within a specific timeframe, enhancing brand visibility and credibility.
Customer Service Department Examples
- Call Time Reduction: A customer service team might set a goal to decrease the average call handling time to under five minutes while maintaining high customer satisfaction ratings. This could involve streamlining processes and providing additional training for representatives.
- Customer Satisfaction Improvement: An objective could be to increase customer satisfaction scores by 30% over the next year through enhanced training programs, better resource allocation, and regular feedback mechanisms.
- Issue Resolution Speed: The team may aim to resolve 90% of customer issues within the first contact, promoting efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Human Resources Examples
- Employee Engagement Initiatives: The HR department might set objectives to improve employee engagement scores by 20% by hosting quarterly team-building events or implementing feedback surveys.
- Training Programs: An objective could be to develop and launch three new training programs aimed at skill enhancement within the next year, ensuring employees are equipped for career advancement.
- Recruitment Efficiency: The HR team may aim to reduce the time-to-hire metric from 45 days to 30 days by refining recruitment processes and utilizing technology for better candidate screening.
Company-Wide Performance Examples
- Revenue Growth Targets: A company may set an overarching goal of increasing revenue by 15% over the fiscal year, requiring all departments—sales, marketing, finance—to align their objectives towards this common target.
- Sustainability Goals: An organization might establish objectives related to reducing its carbon footprint by 25% within five years, involving multiple departments in implementing eco-friendly practices.
- Innovation Initiatives: As part of its growth strategy, a company could aim to launch two new products each year, necessitating collaboration between R&D, marketing, and production teams.
Benefits of MBO for Organizations
Alignment of Goals
MBO creates a unified path for everyone in the organization by ensuring that individual and team objectives directly support the company’s overarching goals.
When leadership establishes clear organizational objectives, every department, team, and employee aligns their efforts to achieve those same targets. This alignment prevents confusion, redundancy, and misdirected efforts, keeping the organization focused on what matters most.
Employees understand how their work contributes to the company’s mission, which fosters a sense of purpose and cohesion.
MBO helps organizations eliminate silos, bringing departments together under a shared vision and creating a collective drive for success.
Enhanced Motivation
MBO’s focus on setting personal, measurable goals for each employee plays a powerful role in enhancing motivation. Employees feel more engaged when they see their goals clearly defined and achievable, understanding that each accomplishment contributes to both their personal growth and the company’s success.
This connection between individual and organizational success fosters intrinsic motivation, as employees feel they are part of something larger.
When employees see their progress and hit milestones, their sense of accomplishment grows, fueling a continuous cycle of motivation and engagement.
MBO taps into this drive by encouraging employees to confidently reach their goals, knowing they have a meaningful impact on the company’s overall performance.
Clear Performance Metrics
With MBO, organizations benefit from transparent, objective metrics that make evaluating success straightforward and fair. When managers and employees set SMART goals, they establish clear, quantifiable criteria that everyone understands.
This objectivity removes ambiguity from the evaluation process, ensuring employees know exactly how their performance will be assessed.
Managers no longer have to rely on subjective judgments; instead, they measure success based on concrete outcomes. Employees feel more secure and motivated when they understand the criteria for success, creating a level playing field that fosters trust and mutual respect.
Clear metrics allow organizations to make informed decisions about rewards, promotions, and areas for improvement, creating a culture of transparency and fairness.
Improved Communication and Collaboration
The MBO process fosters a culture of open communication and collaboration, bringing employees and management together through regular discussions and feedback. MBO emphasizes ongoing dialogue, where managers and employees frequently check in to discuss progress, challenges, and adjustments.
These conversations build trust, creating an environment where employees feel comfortable sharing ideas, seeking support, and tackling obstacles collaboratively. Managers gain real-time insights into their team’s needs, strengths, and potential issues, enabling them to provide timely guidance.
This regular communication strengthens relationships, builds camaraderie, and ensures everyone stays on the same page. MBO helps organizations create a supportive and responsive work culture by promoting collaboration and open dialogue.
Higher Accountability
MBO increases accountability across all levels of an organization, empowering employees to take ownership of their goals. When employees have a clear set of objectives, they feel responsible for their progress and motivated to meet or exceed expectations.
MBO shifts the mindset from merely completing tasks to actively achieving results, encouraging employees to take initiative and exercise their problem-solving skills.
Managers hold employees accountable based on predefined metrics, which creates a fair, structured approach to evaluating performance. This heightened accountability drives a sense of pride and responsibility, as employees feel in control of their contributions and understand how they impact the company’s success.
With MBO, accountability becomes a source of empowerment, fostering a workforce dedicated to achieving meaningful outcomes.
Potential Challenges and Limitations of MBO
Rigid Goal-Setting
One of MBO’s primary challenges is its structured approach to goal-setting, which can sometimes lead to rigidity. MBO requires setting clear, specific objectives at the beginning of each cycle, which creates a strong focus but can hinder flexibility.
In dynamic industries, goals may need frequent adjustments to respond to new market demands, technological advancements, or unexpected obstacles. If teams become overly fixated on achieving their initial goals, they may struggle to adapt, missing valuable opportunities or failing to address emerging priorities.
Organizations need to balance the precision of MBO goals with flexibility, allowing teams to pivot when circumstances change.
Time-Consuming Process
The MBO process demands a significant investment of time and effort from both managers and employees. Setting detailed, measurable objectives for each individual, conducting regular progress reviews, and evaluating results require consistent focus and resources.
This level of structured goal-setting can become cumbersome and overwhelming for large organisations or teams with complex roles.
Managers may find it challenging to maintain the pace of regular check-ins while balancing other responsibilities, and employees may feel bogged down by frequent evaluations.
To prevent MBO from becoming an administrative burden, organizations need to streamline processes where possible and allocate time for goal management without disrupting productivity.
Dependence on Clear Communication
Effective communication stands as a crucial pillar of MBO, yet it also represents a potential vulnerability.
In MBO, managers and employees rely on open dialogue to set realistic goals, provide feedback, and review progress. Any communication gaps can disrupt alignment and create misunderstandings about objectives or expectations.
Employees who don’t receive clear instructions or timely feedback may struggle to achieve their goals or feel disengaged from the process.
Managers must prioritize consistent communication, creating a space for employees to ask questions, clarify expectations, and voice concerns.
Without this foundation of open communication, the MBO process can lose its effectiveness, as team members may misinterpret objectives or miss out on valuable guidance.
Risk of Short-Term Focus
Another limitation of MBO is the potential to develop a short-term focus, where teams prioritize immediate goals over long-term strategies. MBO emphasizes achieving specific, measurable objectives within a defined timeframe, which can inadvertently lead employees to concentrate solely on the present.
When teams become overly focused on hitting short-term targets, they may neglect broader, long-term goals that drive sustainable growth and innovation. This short-sighted approach can hinder strategic planning, as teams prioritize immediate results at the expense of the company’s future direction.
Managers need to carefully balance short-term objectives with the company’s long-term vision, encouraging employees to think strategically even as they work toward immediate goals.
Best Practices for Successful MBO Implementation
Align MBO with Organizational Vision
Aligning all MBO goals with the organization’s vision ensures that every objective, from the highest company-wide targets to individual performance goals, contributes to the company’s long-term success.
Managers and leaders should establish a clear link between strategic objectives and department or employee goals, promoting a unified purpose across the organization.
Employees who understand how their personal goals directly support the company’s mission feel more engaged and motivated to deliver.
This alignment transforms daily tasks into meaningful contributions, reinforcing the organization’s core values and strategic goals at every level.
Use SMART Goals Consistently
SMART goals—Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-Bound—form the foundation of effective MBO. Consistently setting SMART goals creates clarity and accountability, as every team member knows precisely what they are working toward and how success will be measured.
Specificity removes ambiguity, while measurable criteria allow employees and managers to track progress confidently. Setting achievable targets ensures employees feel challenged yet capable of reaching their goals.
By maintaining relevance, SMART goals stay in sync with the organization’s priorities, and time-bound criteria establish deadlines that keep everyone on track.
Leaders must reinforce SMART goal-setting practices to create an environment of clear, achievable expectations, enhancing team motivation and focus.
Encourage Open Dialogue
Fostering open dialogue between managers and employees is essential for effective MBO. When employees feel comfortable discussing their goals, progress, and any challenges they face, they become more proactive and engaged in the goal-achievement process.
Managers should prioritize regular check-ins that create space for feedback, questions, and guidance. This approach makes employees feel supported, strengthens trust, and empowers teams to collaborate openly.
By encouraging honest conversations, MBO turns goal-setting into an interactive process, where employees and managers work together to overcome obstacles and celebrate progress.
Open dialogue also allows leaders to stay informed about team dynamics, helping them to provide targeted support and guidance.
Integrate Flexibility
Integrating flexibility within MBO helps organizations respond effectively to shifting market conditions, emerging challenges, or priority changes. While the MBO framework emphasizes setting and achieving specific objectives, adapting goals as circumstances evolve is essential.
Managers should encourage teams to remain open to adjustments, viewing goals as dynamic rather than static.
By building flexibility into the MBO process, organizations enable employees to pivot quickly when needed, maximizing their responsiveness and resilience.
This adaptability preserves the relevance of MBO goals and ensures that the company remains competitive and agile, regardless of external or internal changes.
Regular Review and Adaptation
Regularly reviewing and adapting MBO goals keeps teams aligned with their targets and prevents goals from becoming outdated. Managers should conduct periodic progress reviews, ideally monthly or quarterly, to assess achievements, identify roadblocks, and recalibrate objectives as needed.
This practice reinforces accountability, ensuring that each employee remains on track and motivated.
Reviews also allow employees to share updates, discuss accomplishments, and seek guidance, creating a culture of continuous improvement.
Organizations can respond to feedback, leverage new insights, and refine goals to drive sustained growth and performance by treating goals as evolving objectives rather than fixed endpoints.
Comparing MBO to Other Goal-Setting Frameworks
| Attribute | Management by Objectives (MBO) | Objectives and Key Results (OKRs) | Balanced Scorecard (BSC) | SMART Goals |
| Focus | Individual performance | Team alignment | Organizational strategy | Goal clarity |
| Goal Setting Process | Collaborative | Flexible | Structured | Defined criteria |
| Measurement | Performance against objectives | Quantifiable key results | Multiple perspectives | Specific metrics |
| Adaptability | Less flexible | Highly adaptable | Moderate adaptability | Limited adaptability |
| Time Frame | Often annual | Usually quarterly | Varies | Varies |
FAQs
-
What are the three main types of objectives in MBO?
MBO objectives fall into three primary categories:
- Strategic Objectives: These long-term goals reflect the company’s overarching mission and vision, serving as the foundation for organizational growth and competitive positioning. Strategic objectives usually extend over multiple years, focusing on future success, brand reputation, or market leadership.
- Tactical Objectives: Tactical objectives support strategic objectives and have a shorter timeline, often ranging from a few months to a year. These objectives break down strategic goals into actionable, intermediate targets for departments or teams, guiding efforts that push the company toward its long-term goals.
- Operational Objectives: Operational objectives focus on the day-to-day activities that keep the business running efficiently. These objectives are often specific to individual roles or teams and aim to maintain a steady workflow, improve efficiency, or ensure consistent customer satisfaction.
Each type of objective in MBO should be realistic, measurable, and interconnected, ensuring that all employees contribute to the company’s overall success and customer experience.
-
Is the MBO process time-consuming?
The initial stages of implementing an MBO program can require significant time and planning, as it involves careful goal-setting, defining objectives, and training managers and employees on the process. However, this upfront investment pays off over time. With clear objectives, ongoing monitoring, and regular feedback, MBO reduces inefficiencies, streamlines decision-making, and increases employee alignment with company goals. In the long run, MBO saves time by minimizing misunderstandings and ensuring that everyone works towards shared objectives, making the organization more productive and cohesive. - What are the four key steps in the Management by Objectives process?
The MBO process consists of four essential steps:
- Setting Objectives: Managers and employees collaborate to define clear, measurable goals that align with both individual roles and the company’s strategic objectives.
- Developing Action Plans: Each employee creates a plan detailing the specific actions they will take to meet their objectives. Action plans outline the resources, steps, and timelines required to achieve each goal.
- Monitoring Progress: Managers and employees conduct regular check-ins to track progress, provide feedback, and adjust action plans as necessary. This ongoing monitoring helps address issues early and keeps everyone on course.
- Evaluating Performance: At the end of the goal cycle, managers review individual and team performance against the defined objectives. This evaluation not only assesses outcomes but also identifies areas for improvement and potential rewards.
Following these steps helps MBO align personal objectives with company-wide goals, enhances decision-making, and promotes accountability across all levels of the organization.
-
How can Human Resources support effective MBO implementation?
Human Resources (HR) plays a pivotal role in the successful implementation of MBO by:
- Communicating Program Benefits: HR can help employees understand the value of MBO by clearly explaining its purpose and benefits. This encourages employee buy-in and supports a smoother adoption process.
- Training Managers on Goal-Setting: HR provides essential training for managers on setting realistic, achievable objectives that align with the MBO model. Proper training ensures consistency and clarity in goal-setting across departments.
- Aligning Performance Reviews with MBO Goals: HR can design performance evaluations around MBO objectives, ensuring that appraisals reflect both individual achievements and contributions to organizational success.
- Leveraging Internal Communication Channels: HR can use tools like social media, email newsletters, or internal portals to keep employees informed, motivated, and engaged in the MBO process. Regular updates and success stories shared company-wide reinforce the MBO approach and celebrate progress.