What is SaaS?

By end of 2025, 85% of all business applications are anticipated to be SaaS-based, up from 70% in 2023. This highlights a significant shift towards cloud-based solutions.
But what is SaaS?
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a model for distributing software in which applications are hosted by a cloud provider and made accessible to end users via the Internet. In this framework, an independent software vendor (ISV) may engage a third-party cloud provider to manage the application’s hosting.
The software vendor may also serve as the cloud provider for larger companies like Microsoft.
SaaS is one of the three primary categories of cloud computing, alongside Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS). It is utilized by diverse users, including IT professionals, business users, and individual consumers.
SaaS offerings include various products, from personal entertainment services like Netflix to sophisticated IT tools. Unlike IaaS and PaaS, SaaS solutions are often marketed to both business-to-business (B2B) and business-to-consumer (B2C) markets.
The global SaaS market was valued at approximately $273.55 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $317.55 billion in 2024, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.4% from 2024 to 2032, potentially hitting $1,228.87 billion by 2032.
How does SaaS work?
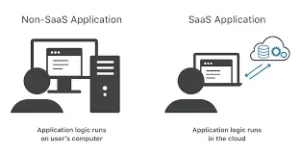
Software as a Service (SaaS) operates as a cloud-based software delivery model that allows users to access applications over the Internet without needing local installation.
Here’s how SaaS works:
Core Functionality of Saas
- Cloud Hosting: SaaS applications are hosted on the servers of a cloud service provider (CSP), such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure. Users access these applications via a web browser, eliminating the need for local installations.
- Subscription Model: Instead of purchasing software outright, users typically subscribe to SaaS applications monthly or annually. This model allows for flexibility in usage and costs, as businesses only pay for what they need.
- Multi-Tenant Architecture: SaaS solutions often utilize a multi-tenant architecture, meaning a single instance of the application serves multiple users or organizations while keeping their data separate. This setup allows for efficient resource management and easier updates.
Architecture of SaaS
Multi-tenant architecture is a major feature of Software as a Service. It allows multiple customers to access and use a single version of an application with the same coding and configuration. In this configuration, hardware, a network, design codes, and an operating system may be included.
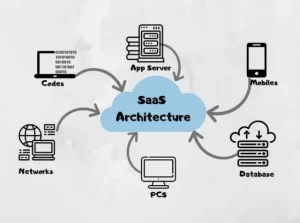
Scalability is the most essential factor in designing a SaaS solution. It is necessary for the smooth installation and usage of the application on numerous devices.
In some cases, SaaS providers extend an updated or test version of the application for customer use. SaaS providers configure and customize different software versions for their customer sites in such scenarios.
Advantages for Businesses using SaaS
SaaS provides several advantages with various attributes and an effortless user experience.
Here are some of the main characteristics of SaaS –
Ease of Accessibility
SaaS simplifies user experience by providing flexible accessibility through interfaces and devices. It can run through an internet browser and does not require specific operating systems for access.
For example, let us consider the software Juntrax by Juntrax Solutions. This SaaS-based business operations software offers comprehensive and user-friendly management assistance for SMEs and startups. Because it is SaaS-based, users can easily access it on system interfaces such as Windows, Mac, Linux, iOS, or Android.
This flexibility and versatility allow SaaS applications to be accessed even outside office premises or on different devices like computers, laptops, tablets, iPads, and mobile phones. This removes the tension of checking the software’s compatibility and provides a smooth and adjustable work environment for both employees and administrators.
Smooth and fuss-free updates
SaaS applications run on a cloud-based interface. This allows easy updates on a large scale without causing any hindrance or inconvenience to the user. It allows updates to happen simultaneously while the business processes are being carried out.
Unlike on-premise software, it does not require a compatibility check or work to stop while the systems settle updates. It also allows easy and prompt security testings before routine updates and effortlessly allows the patches to be applied through the system.
The SaaS model is the perfect option to prevent the loss of work and time that occurs with on-premise or system-specific software.
Hardware
The best attribute of SaaS is that it does not require any additional investment in hardware or other logistics.
Unlike software-as-a-service applications, on-premise software is system-specific and requires special configuration, external safety aid, and a set of different equipment for assistance. In addition to these requirements, it also needs additional servers and network switches to form a smoothly functioning IT structure.
SaaS applications come with two necessities: an Internet connection and a device where they can run. This device can be a laptop, a computer, a tablet, or even a phone. SaaS also inculcates scalability to the system.
For example, if the enterprise wishes to add more users to their system or reduce them, they can easily adjust that in their billing plan.
Saving and storage
On-premise software requires a backup special generation and consumes considerable space while storing all data. This creates a need for investment in incredible backup aids.
This is where Software as a service serves as the most convenient and user-friendly option. It inherently works on a cloud-based interface and, by default, stores all data on the cloud.
SaaS providers conserve this data through security measures like login credentials. Users can access the data as per their requirements and convenience. It occupies no additional space in the device and provides a user-friendly experience.
Unlike system-specific software, in the case of software as a service, the employee can easily shift from one device to another without losing data.
Data and analytics
The centralized platform makes it easy to capture data and provide it for analytics. SaaS software is usually equipped with reporting and intelligence tools and visualizations that provide valuable insights into business operations, allowing streamlined workflows and realized efficiency savings.
Access depends on a paid subscription, so the vendor does not need to worry about piracy, which might otherwise damage access and pricing.
Adoption Trends of SaaS Across Industries
The adoption of SaaS has surged across various industries, driven by the need for flexibility, cost efficiency, and remote accessibility.
Key trends include:
- Widespread Usage: Over 80% of businesses utilize at least one SaaS application, with projections indicating that nearly all companies will adopt SaaS solutions by the end of 2024.
- Industry-Specific Growth: Industries such as technology, healthcare, finance, and education lead the way in SaaS adoption. For instance, the CRM market alone is expected to reach $60 billion by 2025, showcasing the demand for SaaS solutions in customer relationship management.
- Remote Work Influence: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the shift to SaaS as organizations adapted to remote work environments. This trend is expected to continue, with productivity-focused SaaS solutions projected to grow significantly.
- Investment and Innovation: SaaS start-ups received substantial venture capital investments, highlighting confidence in the model’s growth potential. The market is anticipated to reach $344 billion by 2027, reflecting the increasing reliance on cloud-based solutions.
What are some common examples of Software as a Service?
Any service which is centralized over an online platform and can be accessed on all devices is termed as a SaaS. Facebook, Instagram, and Snapchat are very common and prominent examples of this.
Other examples of SaaS are BigCommerce, Salesforce, Dropbox, MailChimp, ZenDesk, DocuSign, Slack, Hubspot, and Juntrax.
Google apps like Google Meets, Slides, Maps, and Drive also fall into the SaaS category.
SaaS applications can be accessed through subscriptions instead of a properly paid license upfront. There are also options for customized SaaS services for personal use.
Companies like Juntrax Solutions add features and tools to their systems according to their clients’ requirements.
SaaS vs. IaaS vs. PaaS
SaaS is one of the three primary cloud service models, alongside IaaS and PaaS. Each model involves cloud providers offering customers their own hosted data center resources via the Internet.
The key distinction among these models lies in the level of product completeness. SaaS products are fully managed applications that are ready for use. In contrast, IaaS primarily focuses on outsourcing data center resources, while PaaS provides a development platform and various tools hosted in the provider’s data center.
| Feature | SaaS | IaaS | PaaS |
| Definition | Software delivered via the internet, subscription-based. | Virtualized computing resources over the internet. | A platform for developing, testing, and deploying applications. |
| Typical Users | Businesses, end-users, and organizations. | IT departments, developers, and enterprises. | Developers and IT teams. |
| Payment Model | Subscription fees are based on usage. | Pay-as-you-go model. | Subscription or usage-based pricing. |
| Customization | Limited customization options. | High customization with control over resources. | Moderate customization based on the platform. |
| Maintenance | Provider handles all maintenance and updates. | The user manages OS, applications, and middleware. | Provider handles infrastructure maintenance. |
| Scalability | High scalability for user needs. | Flexible scalability for workloads. | Scalability based on application demand. |
| Use Cases | CRM, ERP, and collaboration tools (e.g., Salesforce, Google Workspace). | Web hosting, storage, and backup solutions (e.g., AWS EC2, Google Cloud). | Application development, API development (e.g., Heroku, Google App Engine). |
| Security Concerns | Data security and internet dependency. | Network security and management responsibilities. | Security of data and applications. |
| Examples | Salesforce, Microsoft Office 365, Netflix. | Amazon EC2, Google Cloud Compute, Microsoft Azure. | Heroku, Google App Engine, Microsoft Azure App Service. |
Challenges Businesses Face When Adopting SaaS and How to Overcome Them
Despite the rapid growth, the industry faces challenges such as data security concerns, with many organizations struggling with SaaS misconfigurations that can lead to data breaches.
Understanding these challenges and how to effectively address them can ensure a smoother integration and maximize the benefits of SaaS solutions.
Data Security Concerns
One of the primary concerns businesses face when adopting SaaS is ensuring the security of their data. With sensitive information being stored offsite, companies must be vigilant about protecting it from unauthorized access and breaches.
To mitigate these risks, choose SaaS providers that prioritize security by offering end-to-end encryption, regular security audits, and compliance with industry standards such as GDPR or HIPAA.
Additionally, implementing robust internal data protection policies and user access controls can further safeguard your data.
Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating SaaS solutions with existing systems can be a complex process, often leading to compatibility issues or disruptions in workflow. This challenge can hinder productivity and delay the benefits of adopting new software.
The key to overcoming integration challenges is thorough planning and assessment. Before adoption, comprehensively analyze your current systems and identify potential integration points.
Collaborate with your SaaS provider to develop a tailored integration strategy that includes APIs or middleware solutions, ensuring seamless communication between systems.
Additionally, consider phased implementation to allow for gradual adaptation and minimize disruptions.
Cost Management
While SaaS solutions often reduce upfront costs, businesses can face challenges in managing ongoing expenses, especially with unpredictable subscription fees and scalability requirements.
Effective cost management begins with a clear understanding of the total cost of ownership. Evaluate the pricing models of different SaaS providers and choose one that aligns with your budget and usage patterns.
Opt for flexible pricing plans that allow scalability without incurring significant additional costs. Regularly monitor usage to optimize your subscription levels and eliminate unnecessary expenses.
Implementing these strategies can help maintain cost efficiency and maximize the return on investment in SaaS solutions.
Important Tips for SaaS Startups
Software as a service is evolving as a very potential market daily.
It is estimated that by 2035, 80% of all corporate ventures will switch to SaaS. With this increasing prospect, numerous startups aspire to ace the field with their ideas.
However, before entering every field, some essential factors must be worked upon.
Marketing is the ticket to earn customers
Marketing is a very significant aspect of undertaking an endeavor.
You need to brainstorm ideas that can boost your brand’s visibility and help it reach the masses. Reaching your target audience requires a proper plan of action. Look for innovative and appealing ideas.
Try to engage with organic forms of marketing. Conduct research, work with creative campaigns, and organize brainstorming sessions. Keep yourself open to ideas and try to read the perspective of your target audience.
Do not ignore your finances
Due to your restricted budget, you will encounter numerous constraints as a startup. Strive to reach out to funding organizations and propose your idea to them.
Manage your finances carefully and allocate them to essential expenditures first.
Before making any transaction, question whether your startup urgently requires it. Good financial management from the very beginning will help you manage and plan your future finances professionally and maturely.
The strategy is the key
Always formulate a strategy before instigating your successive stride. Organize your intentions and contemplate them before putting them into action.
Properly document and arrange your plans. After applying your strategy, assess it in relation to your startup’s growth and benefits.
If you feel that the performance of your enterprise is still stagnant, look for loopholes and develop updated strategies.
This hit-and-trial method will help you reach a suitable plan.
Form a team
Divide roles and formulate a team. Dividing responsibilities can help you manage better and yield better results. Having a well-managed team can help you walk through the most challenging times of your journey and give a sturdy foundation to your venture.
Future of SaaS
Market analysts are optimistic about the future of Software as a Service (SaaS) and project significant growth in the coming years.
Gartner projects that the SaaS market will reach approximately $232 billion by 2023, reflecting a growth rate of 17.7% from the previous year.
Furthermore, analysts anticipate that the industry will expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 18.7%, potentially reaching a staggering $908.21 billion by 2030.
Several key innovations are driving this growth:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration: The rise of AI solutions is transforming SaaS applications, with 35% of businesses currently utilizing AI in their SaaS offerings. This figure is projected to increase to 42% shortly. AI enhances adaptive intelligence capabilities, allowing applications to learn from user interactions and optimize functionality.
- Autonomous IT Management: Advances in AI and machine learning facilitate more autonomous management of cloud applications, reducing reliance on human intervention and streamlining operations.
- Emerging Technologies: Beyond AI, various adaptive technologies such as chatbots, digital assistants, the Internet of Things (IoT), blockchain, virtual reality, and augmented reality are becoming integral to SaaS solutions. These technologies are essential for fostering digital innovation and enhancing the service offerings of forward-thinking providers.
- Vertical SaaS Solutions: The market for vertical SaaS—tailored solutions for specific industries—is projected to grow significantly. Estimates suggest it could surpass $157 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 23.9%. This trend reflects a shift from generic applications to specialized solutions that address unique industry challenges.
- Cross-Business Connectivity: SaaS providers are expected to enhance their offerings with APIs and integrations that facilitate cross-departmental visibility and collaboration as organizations increasingly seek interconnected solutions.
FAQs on SaaS
Q: What is SaaS in simple terms?
A: SaaS, or Software as a Service, is a cloud-based service where instead of downloading software on your desktop PC or business network to run and update, you access an application via an internet browser. The software application could be anything from office software to unified communications among a wide range of business apps that are available.
Q: What is an SaaS example?
A: An example of SaaS is Google Workspace (formerly G Suite), which includes Google Docs, Google Sheets, and Google Drive. Cloud-based software providers deliver these solutions over the internet, allowing you to access and use them through your web browser without needing to install anything on your computer.
Q: Is Netflix a SaaS?
A: Yes, Netflix can be considered a SaaS. As a subscription-based streaming service, it provides the software (in the form of a streaming app) that delivers video content over the internet.
Q: Is YouTube a SaaS?
A: No, YouTube is not typically categorized as a SaaS. YouTube primarily serves as a Platform as a Service (PaaS) by providing the infrastructure that enables content creators to upload, store, and stream their videos to end users.
Q: Is WhatsApp a SaaS?
A: Yes, WhatsApp can be considered a SaaS. It is a cloud-based messaging service that allows users to send messages, make voice and video calls, and share files over the internet.
Q: Is LinkedIn a PaaS or SaaS?
A: LinkedIn is considered a SaaS. It is a platform that offers business and employment-oriented services through its website and mobile apps, providing software functionalities like networking, job searching, and professional interactions.
Q: What is the difference between cloud and SaaS?
A: The term “cloud” refers to a broad range of services delivered over the internet, including storage, processing power, and applications. SaaS providers deliver software applications over the internet, and users access these applications via a web browser. In other words, SaaS services use the cloud, but the cloud can provide other types of services besides SaaS.
7 thoughts on “What is SaaS?”
Comments are closed.
Everything is very open with a precise clarification of the issues.
It was definitely informative. Your website is very helpful.
Many thanks for sharing!
I am really delighted to glance at this web site posts which includes lots of helpful information, thanks for providing these statistics.
Very good written post. It will be useful to anyone who utilizes it, as well as yours truly :). Keep up the good work – looking forward to more posts.
As I website possessor I believe the content material here is rattling wonderful , appreciate it for your efforts. You should keep it up forever! Best of luck.
I like what you guys are up also. Such smart work and reporting! Keep up the excellent works guys I have incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it’ll improve the value of my site 🙂
very nice post, i actually love this web site, carry on it