Multigenerational Workforce: Challenges, Benefits, and Solutions

In today’s workplace, employees from different generations work together, creating a multigenerational workforce. This diversity offers many advantages, like unique perspectives and stronger teamwork, but it also comes with challenges. Understanding how to embrace and manage generational differences can help businesses thrive.
This guide covers the benefits of a multigenerational workforce, common challenges, and practical strategies for building a successful, inclusive work environment.
What is a Multigenerational Workforce?
A multigenerational workforce includes employees from several age groups working together. Each generation brings unique qualities and working styles, making diversity both an asset and a challenge.
Generational Definitions
| Generation | Birth Years | Key Traits |
|---|---|---|
| Silent Generation | 1928 – 1945 | Loyal, disciplined, value hierarchy |
| Baby Boomers | 1946 – 1964 | Hardworking, focused on stability and teamwork |
| Generation X | 1965 – 1980 | Independent, adaptable, value work-life balance |
| Millennials (Gen Y) | 1981 – 1996 | Tech-savvy, collaborative, purpose-driven |
| Generation Z (Gen Z) | 1997 – 2012 | Digital natives, innovative, value inclusivity |
Understanding these traits is the first step to bridging generational gaps and creating a cohesive work environment.
Benefits of a Multigenerational Workforce
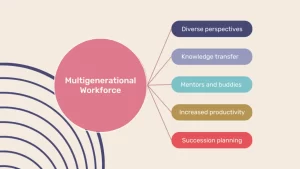
Having employees from different generations working together can benefit organizations in many ways:
1. Diverse Perspectives
Each generation has unique experiences and ideas. Older employees bring wisdom and expertise, while younger generations offer fresh perspectives and innovative solutions.
2. Innovation and Creativity
Generational diversity encourages creative problem-solving. When employees with different skills and mindsets collaborate, they generate better ideas and solutions.
3. Wide Range of Skills
From technological expertise to leadership abilities, a multigenerational team provides a balanced mix of skills. For example, digital natives excel in social media, while senior employees share institutional knowledge.
4. Knowledge Transfer and Better Collaboration
Working side by side with different age groups builds stronger teams. Employees learn from each other and develop mutual respect.
5. Improved Productivity
Catering to the needs of multiple generations helps create a positive workplace where employees feel valued, leading to higher satisfaction and retention rates.
6. Succession Planning
One of the major benefits of a multigenerational workforce is a better succession planning.
Get your FREE Trial of Juntrax
Challenges of a Multigenerational Workforce
While the benefits are clear, managing a multigenerational workforce also presents challenges:
1. Different Communication Styles
Each generation has its own way of communicating. Older generations may prefer face-to-face discussions, while younger employees favor emails or instant messaging.
2. Varying Working Styles
Baby Boomers might prefer structured processes, whereas Millennials and Gen Z thrive in flexible environments. Balancing these preferences can be tricky.
3. Technology Gaps
Younger employees adapt quickly to new technologies, but older employees may need extra training and support to stay updated.
4. Generational Biases
Stereotypes about different age groups can lead to misunderstandings and conflict. For example, younger workers may view older colleagues as resistant to change, while older employees may see younger generations as inexperienced.
5. Meeting Diverse Needs
Each generation has unique priorities. For instance, younger generations may seek career growth, while older employees might value stability and retirement planning.
Also Read: What is Human Resource Management (HRM)?
How to Embrace a Multigenerational Workforce
To make the most of generational diversity, organizations need strategies that support collaboration and inclusivity. Here’s how to manage and embrace a multigenerational workforce:
1. Encourage Open Communication
Promote a culture of transparency where employees feel comfortable sharing their ideas and concerns. Use a mix of communication tools to meet everyone’s needs, such as in-person meetings, emails, and apps like Slack or Zoom.
2. Create Mentorship Opportunities
Pair older employees with younger employees to exchange knowledge. Senior workers can offer guidance and mentorship, while younger staff can help with technology and modern trends.
3. Offer Flexibility
Implement flexible work arrangements, such as remote work or adjustable hours. This caters to all age groups, especially younger generations who value work-life balance.
4. Provide Learning and Development
Offer training programs to bridge skill gaps. For example, digital training for older employees and leadership development for younger employees.
5. Recognize and Celebrate Contributions
Celebrate achievements across all age groups to show employees they are valued. This fosters respect and boosts morale.
6. Build Collaborative Teams
Encourage diverse teams where employees from different generations work together. Collaboration helps break down stereotypes and improves teamwork.
The Role of Generational Diversity in the Workplace
Generational diversity strengthens workplace culture by encouraging respect and collaboration. When employees feel valued and included, they perform better, stay motivated, and contribute to a positive work environment.
Organizations that embrace generational diversity can foster innovation, retain top talent, and create a dynamic workplace that thrives in today’s competitive market.
Future Trends in Managing Generational Diversity
As workplaces evolve, managing generational diversity will become even more important. Key trends include:
- Hybrid Work Models: Combining remote and in-office work to suit everyone’s preferences.
- Wellness Initiatives: Offering mental health and wellness programs that benefit all generations.
- AI and Technology: Using tools like AI to personalize employee experiences and improve communication.
Conclusion
A multigenerational workforce is an asset for any organization. By embracing generational diversity, businesses can unlock the full potential of their teams. While challenges like communication differences and technology gaps exist, thoughtful strategies—like mentorship programs, flexible work policies, and inclusive training—can overcome these barriers.
When organizations create a workplace where employees from all generations feel respected and supported, the results are undeniable: better innovation, stronger teamwork, and long-term success.
Ready to embrace generational diversity? Start by implementing strategies that foster inclusivity, respect, and collaboration across all age groups.
FAQs About Multigenerational Workforce
1. What is a multigenerational workforce?
A multigenerational workforce consists of employees from different age groups—such as Baby Boomers, Millennials, and Gen Z—working together within an organization.
2. What are the benefits of a multigenerational workforce?
Benefits include diverse perspectives, enhanced innovation, a broader range of skills, and improved collaboration among employees.
3. What are the challenges of managing a multigenerational workforce?
Challenges include differences in communication styles, working preferences, technology gaps, and generational stereotypes.
4. How can companies support a multigenerational workforce?
Organizations can support generational diversity by encouraging open communication, offering mentorship programs, and providing flexible work arrangements.
5. Why is generational diversity important in the workplace?
Generational diversity fosters innovation, strengthens teamwork, and creates a positive workplace culture where employees feel valued and motivated.
6. How can technology help bridge generational gaps?
Technology tools like collaboration platforms, digital training modules, and analytics software can improve communication, skill-building, and inclusivity among employees.